In today’s time, it is imperative for every sector to focus not only on better data handling and governance solutions but also on the steadfast use of data that is long untamed. The findings of a study indicate that data-driven organizations are 23 times more likely to acquire more customers than their peers.
Insurance is a data-driven industry. Every day, there are new players in the competition, and each one of them has a mine of data, but only the ones converting that data into useful insights and using them in their decision-making can make it a gold mine. According to the findings of a recent study, 86% of insurance companies are working on insurance data analytics mechanisms for optimum predictions of big data reports.
According to a predictive analytics report, current investment in predictive analytics of the Individual Life and Individual Health ecosystem is 70 percent and 40 percent respectively, which is assumed to grow up to 90 percent and 80 percent in just the next two years.
This is the power of data that is being used as a source of strategic decision-making today. But this source of data needs to be unleashed to its full power by procuring insights that will help the insurance companies achieve their long-term goals.
If advanced analytics in insurance is leveraged appropriately, it can revolutionize the insurance business and make their operations resilient and future-ready.
Table of Contents
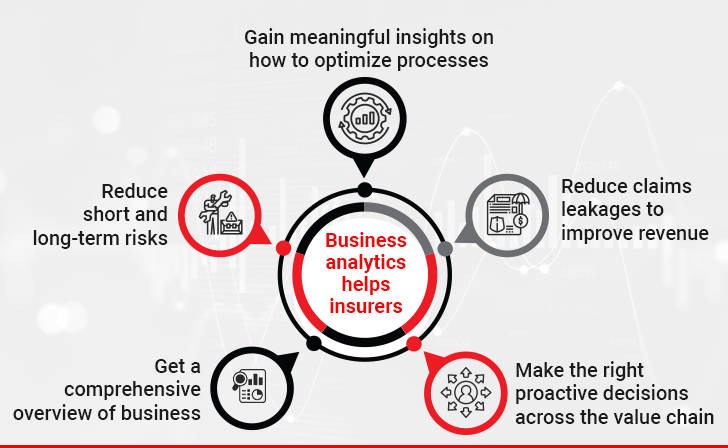
Use of Business Analytics in Insurance
Understanding Data Analytics and How it Benefits Insurers
Challenges in Extracting Value from Data
Use of Business Analytics in Insurance
Understanding Data Analytics and How it Benefits Insurers
Data analytics in the insurance industry involves the methodical use of data to gain insights, make predictions, and enable smarter decision-making. Insurance companies sit on mountains of data. Every policy, claim, and customer interaction generates data. When properly analyzed, this raw data provides insights that drive measurable business outcomes.
So, what makes data analytics powerful for insurers?
- Actionable Insights: Scattered data is analyzed and presented in the form of easy-to-follow charts and graphs. This drives more informed business choices.
- Precision Targeting: Insurers can identify which customers need which products at which stage of their journey. They can create tailored policies based on risk profiles to improve conversions.
- Risk Identification: Insurers see risk patterns that traditional analysis often doesn’t reveal. Precise risk identification boosts underwriting accuracy.
- Fraud Detection: Suspicious claims are flagged before payouts. This reduces financial loss for the insurer.
Insurance has always been a data-driven business. Companies using data analytics solutions have witnessed significant improvements in decision-making underpinned by business intelligence to improve customer conversion. The key benefits offered by data analytics are:
1. Customer Acquisition and Personalization
Customer acquisition through high-quality lead generation has become progressively tougher at a time when information is available at our fingertips and attention is fleeting. Even if you manage to capture the prospect’s attention, tracking lead information from different sources can get tricky through paper and spreadsheet-based processes in place. Such a scenario calls for modernizing legacy systems to centralize information and databases, especially when it relates to core business processes. Insurance data analytics of such unstructured data helps you deep dive into the customer behavior patterns and common demographics and characteristics, and target the right customer segments to create market opportunities to up-sell and cross-sell.
Further, data analytics-enabled tools like CRM and agency management systems enable businesses to extract valuable insights from reports that reveal the customer journey, right from search to conversion. It helps them understand customer behavior and enables the marketing department to target the right personalized messages for warming up leads.
2. Meaningful and Deeper Customer Engagement
Satisfied customers drive revenue and brand equity of businesses. Enhanced customer satisfaction is the result of initiatives on advocacy, referral marketing, and brand identity creation. If a business is successful in fulfilling customer expectations, it will automatically register accelerated and unprecedented growth. According to a McKinsey report, satisfied policyholders are 80% more likely to opt for policy renewals.
An insurance company that can correctly predict the needs of prospective customers by looking through data trends and the complete view of a customer’s previous interactions with the brand has much more potential to make the sale than an insurance company just using conventional methods of selling. Analytics in insurance provides the capability to go through IoT-enabled data to understand the needs, desires, and advice of their customer. Similarly, analysis of the existing customer data can also offer prescriptive insights into improving customer satisfaction. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) solutions can prove to be invaluable in such situations, as they can offer detailed and granular insights into the customer’s current and future requirements.
Harness the Power of Data Analytics for Accelerated Business Advantages
3. Mitigating Claims Fraud
Claims fraud continues to be a major challenge in the insurance sector. The Coalition of Insurance Fraud estimates that $80 billion is lost annually from fraudulent claims in the USA alone. Additionally, fraud makes up 5-10% of claims costs for insurers in the North American region. However, insurance companies using data analytics have seen considerable improvements in their fraud detection process. With the application of data analytics, insurance claims fraud detection becomes speedier and more accurate. For example, the history of fraudulent cases is stored in the data trends of an insurance company, and while processing any claim, the insurers can carefully check if the trend is repeated. This, in turn, helps reduce the act of fraud.
Apart from fraud detection, analytics can also be applied for fraud prevention and mitigation. Advanced analytics and claims predictive modeling leverage both business data and information from external third-party sources for identifying potential claims fraud. Even before the submission of the claims, the predictive analytics model can detect individuals who are more likely to submit fraudulent claim reports.
4. Predicting Accurate Risk for Underwriting
Underwriting is a complex task for insurers, and it can be simplified through insurance underwriting analytics. For example, the data trend would predict a higher auto insurance premium for a customer who has been engaged in rough driving than for a customer whose data trend predicts a lesser risk profile. Such data can also come in handy during insurance claims automation as insurers can accelerate the policyholder’s journey from FNOL to recovery.
The application of advanced analytics in the insurance underwriting process encourages underwriters to concentrate on subjective tasks that call for judgment and intuitive decision-making while enabling systems to handle back-office work. Data analytics models can also be used for developing better underwriting rules. This, in turn, contributes to a uniform application of underwriting practices and lesser risks.
5. Streamlined Claims Processing
Data analytics in insurance can have a significant impact on improving the efficiency and accuracy of claims processing. By analyzing historical claims data and utilizing predictive modeling, insurers can automate and streamline the claims assessment process. This leads to faster claims resolution, reduced administrative costs, and improved customer satisfaction. Also, as mentioned earlier, applying data analytics in insurance claims processing can help identify fraudulent claims more effectively. This ensures that legitimate claims are processed promptly while mitigating losses due to fraudulent activities.
6. Enabling Business Growth
One of the important elements of the Insurance domain is quantifying the levels of risk so that it can accelerate business growth. Until recent times, the calculation of this business-critical risk was purely intuitive and largely guesswork. However, with hordes of data now readily available, it is possible to base such assessments on pure data rather than conjectures, and even predict eventualities that can disrupt operations. Accordingly, insurance businesses can analyze this data and plug revenue leakages that could be eating into the business’ profits. In this way, Insurance data analytics acts as an engine for the growth of Insurance companies with its capability in predictive analysis of big data.
7. Improving Regulatory Compliance
The insurance industry is subject to a myriad of regulations and compliance requirements. Data analytics in the insurance industry helps insurers navigate this complex regulatory landscape by providing tools to monitor and ensure adherence to compliance standards. Analyzing data in real-time enables insurers to detect and address potential compliance issues promptly. Furthermore, data analytics for insurance companies can assist in generating comprehensive data and analytics reports and audits, thereby simplifying the compliance reporting process. By leveraging analytics to stay abreast of regulatory changes and proactively address compliance concerns, insurers can avoid penalties, reputational damage, and legal challenges associated with non-compliance.
Challenges in Extracting Value from Data
Data offers many opportunities. However, companies face several roadblocks when they implement data analytics in the insurance industry. These include:
I. Data Quality and Integration
Insurance companies face issues with poor data quality. This creates distrust in the data and weakens faith in analytics.
The industry lacks common data standards. This leads to inconsistencies. Many insurers still use siloed systems and databases. This makes effective data analysis difficult. Poor data integration causes AI models to fail, and automation falls short of its goals.
A majority of insurers use processes, procedures, and legacy systems that are incompatible with modern methods. Old systems and fragmented data create barriers to smooth integration. Some insurers worry about privacy, regulation, and security. This stops them from moving their data to the cloud. It also creates a siloed data environment.
Insurers can implement a unified data governance framework to improve data quality and ensure integration. They can use API-based middleware to connect legacy systems with analytics platforms.
How to Simplify Insurance Claims Processes with Data Analytics
II. Talent Gap
Insurance workers need data skills more than ever before. Yet the industry faces a mounting talent crisis. By 2026, U.S. insurers could lose approximately 400,000 workers through attrition, according to U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projections.
The insurance workforce is aging. This could impede the adoption of new technologies. Many senior employees may not be comfortable working with analytical tools.
Insurance companies now need individuals proficient in data analysis, predictive modeling, and software development. Many of them have to compete with tech giants for these specialized roles.
To close the gap, progressive insurance companies are investing in upskilling programs. Some of them have partnered with universities for specialized training pipelines. Without these interventions, the sector may not be able to fully utilize analytics for risk assessment and customer personalization.
III. Ethical Considerations
The data doesn’t lie, but what if it’s biased from the start? Companies must ensure their decisions take into account fairness, bias, and potential harm to people or groups.
Biased training data represents the most common source of algorithmic unfairness. Historical data frequently mirrors societal biases and stereotypes, which get encoded into AI systems. For example, an insurance algorithm may learn from data that correlates accidents with certain demographic groups instead of actual driving behavior. The outcome? It’ll unfairly charge some people higher premiums.
Left unchecked, these biases lead to discriminatory outcomes, including:
- Unequal pricing with algorithms setting higher premiums for certain groups
- Inadequate coverage where some individuals are denied protection
- Lack of inclusivity with models failing to meet diverse customer needs
AI algorithms aren’t inherently biased. However, when trained on skewed data, they amplify existing biases. Fixing this starts with acknowledging the problem. Insurers must balance accuracy with fairness, ensuring both their methods and outcomes are equitable. To stay on track, companies should regularly audit their algorithms, and the data used to train them, keeping a close eye on fairness.
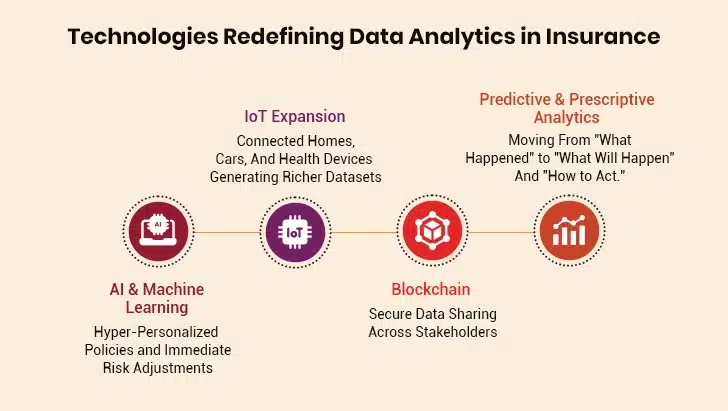
The Future of Business Analytics in Insurance
Several major developments will reshape how insurers use data in the coming years. These aren’t far-off possibilities—they’re already beginning to take shape in forward-thinking companies.
1. AI And Machine Learning
Insurance is moving toward hyper-personalization. Cognitive technologies now process complex data in real-time from active insurance products. In the future, people will buy insurance with minimal human involvement as AI creates instant risk profiles.
Most insurance executives already consider predictive models critical for underwriting’s future. These advances allow insurers to deliver customized policies based on behavioral data. Coverage gets adjusted instantly when risk factors (e.g., policyholder behavior) change.
2. IoT Expansion
Industry experts predict up to one trillion connected devices by 2025. Think about that number for a moment. These devices generate mountains of data that insurers can put to work.
To cite an example, telematic devices installed in cars record driver behavior. Health devices track vital stats. Home security systems monitor when people enter or leave. Each device creates data that helps insurers understand risk better. Today, the industry is shifting from “detect and repair” to “predict and prevent”. In the near future, insurers will help policyholders avoid risks altogether, instead of paying for damages after they occur.
3. Blockchain
Insurance requires trust. Blockchain builds it into the system. This technology creates immutable, transparent records that simplify data sharing across the insurance ecosystem.
The global market for blockchain in insurance will cross $59.90 billion by 2032. Soon, smart contracts will execute policy terms once predefined conditions are met. Imagine filing a claim and receiving payment in minutes. No paperwork. No phone calls. Just automated verification and payment. Going ahead, the technology will boost claims management, fraud prevention, and reinsurance operations.
4. Predictive and Prescriptive Analytics
Insurance data analytics is moving from predictive models to prescriptive insights. Traditional analytics told insurers what happened. Predictive analytics suggests what might happen next. Prescriptive analytics recommends specific actions based on data-driven insights.
The global market for these tools is expected to grow by 24% annually between 2025-2030. Insurers who adopt these technologies won’t just understand risk better; they will know exactly how to manage it.
Conclusion
Data analytics has fundamentally transformed the insurance industry. The strategic use of data analytics for insurance companies helps create personalized experiences, detect fraud with accuracy, and assess risk with precision.
The future promises even greater transformation as AI, IoT, blockchain, and advanced analytics join forces. Soon, we will see personalized policies that adjust automatically to changing conditions and proactive risk management through predictive analysis. There’s no doubt that implementation difficulties exist. However, companies that invest in analytics capabilities now will be better positioned for long-term success.
Insurance industry’s foundation has always been data analysis. Today’s technological capabilities have raised this foundation into something truly transformative. The question no longer remains whether data analytics will reshape insurance, but how quickly companies will adapt to this new reality.