Your customers use ChatGPT to write emails, Alexa to control smart home devices, and Google Assistant to plan vacations. But when they call your insurance company to inquire/claim, they are asked to “press 1 for English.” The experience is frustrating!
This takes policyholders back to the primitive era, where they waited for an agent to address their issues and inquiries. Instead, policyholders want almost instant and accurate responses, irrespective of the time and day. Even though rule-based chatbots can handle thousands of interactions simultaneously, they often fail to provide accurate and personalized responses.
The stark difference highlights a fundamental issue that extends beyond customer satisfaction. It significantly impacts operational cost and efficiency, wherein human adjusters often have to compensate. Thus, insurers require autonomous insurance agents to improve customer service and provide seamless support without missing a beat.

According to Deloitte’s 2025 global insurance outlook, demand for customer-centric experiences has contributed to the popularity of embedded insurance, which is projected to exceed USD 722 billion in premiums globally by 2030. Thus, whether it’s addressing policy-related queries, tracking claims, or offering personalized coverage, AI agents in insurance are making every interaction quicker and more reliable.
Table of Contents
The Limitations of Traditional Chatbots
AI Agents as the Harbinger of Insurance Automation
Real-World Insurance Use Cases of AI Agents
Strategic Benefits for Insurers
The Limitations of Traditional Chatbots
Although chatbots were once considered cutting-edge, their inflexible architecture and limited decision-making capabilities are now a liability. Insurers relying on them now risk falling short on customer expectations and operational performance. Take a detailed look at why chatbots fail to meet the demands of the modern insurance ecosystem:
-
Structural Inflexibility
Traditional chatbots follow predefined conversation flows that collapse if customers deviate from expected patterns. For instance, a commercial client reporting equipment breakdown can’t receive support from scripts made for personal auto claims. These systems force unnatural conversations that frustrate customers and waste agents’ time.
-
Lack of Context
Another major limitation of rule-based chatbots is that they treat each interaction as a separate event. They can’t connect a policyholder’s claim inquiry to their policy history, previous conversations, or current coverage status. Thus, policyholders often need to provide background information repeatedly, whereas agents are unable to deliver comprehensive service due to the lack of context.
-
Integration Isolation
Most chatbots work as standalone applications with limited access to enterprise systems. This integration isolation implies that chatbots can’t simultaneously access policy details, claims history, and payment status to provide complete responses. This creates information silos that undermine the quality of service.
While chatbots helped with early automation and enabled earlier stages of insurance digital transformation, their limitations are increasingly problematic. What the industry needs now is a more adaptive, intelligent, and proactive solution, one that AI agents are uniquely positioned to deliver.
AI Agents as the Harbinger of Insurance Automation
Unlike static chatbots, AI agents can dynamically reason, adapt, and interact across channels and systems. A step ahead of digital assistants, they’re autonomous problem solvers capable of handling complex tasks from start to finish. This new generation of technology marks a profound shift in how insurers engage with customers, handle claims, and optimize operations.
In the agentic AI vs chatbot in insurance debate, the key distinction lies in the AI agents’ ability to understand intent rather than matching keywords. Thus, when a customer says, “My kitchen caught fire and the adjuster never showed up,” an AI agent identifies both issues: a property damage claim and a service complaint. It addresses both at once while coordinating the next steps.
In short, these systems adjust their communication approach to specific situations. For instance, AI agents explain coverage details to first-time homeowners in a manner different from how they discuss commercial liability terms with experienced risk managers.
“Agents are smarter. They’re proactive – capable of making suggestions before you ask for them. They accomplish tasks across applications. They improve over time because they remember your activities and recognize intent and patterns in your behavior. Based on this information, they offer to provide what they think you need, although you will always make the final decisions.”
– Bill Gates, Co-Founder, Microsoft
AI Agents vs. Traditional Chatbots: Capability Comparison Table
| Capability | Traditional Chatbots | AI Agents |
|---|---|---|
| Interaction Style | Scripted, rule-based | Adaptive, intent-driven |
| Context Awareness | Lacks memory of past interactions | Maintains and applies full contextual memory |
| Data Integration | Limited or siloed | Real-time enterprise-wide data access |
| Use Case Complexity | Handles simple, linear tasks | Manages multi-step, high-complexity scenarios |
| Customer Personalization | One-size-fits-all | Tailor communication to individual profiles |
| Scalability | Requires linear staffing for growth | Scales seamlessly with minimal marginal cost |
| Learning and Optimization | Static behavior | Continuously learns and improves |
| Compliance and Auditability | Limited tracking | Full audit trails and explainable decision paths |
To sum up, AI agents can do a lot more than traditional rule-based, scripted chatbots. They’re “proactive” in all their approaches, empowering insurers to ensure regulatory compliance and provide personalized experiences, irrespective of the market dynamics. That said, let’s dive into the concrete, real-world ways these AI agents are already driving transformation across insurance workflows.
Real-World Insurance Use Cases of AI Agents
The fact that theoretical advantages are only as good as their practical applications stands true in the insurance industry. Fortunately, AI agents are already delivering tangible results across claims, servicing, underwriting, and more. Here’s how intelligent agents are solving business-critical problems in live insurance environments:
1. FNOL Automation with Dynamic Intelligence
AI-powered FNOL automation has a revolutionary impact on claims processing. When handling a commercial auto accident involving multiple vehicles, the AI agent collects incident details and evaluates coverage implications across multiple policies. In addition to initiating the inspection processes, the AI agent coordinates with repair facilities.
The best part is that all this happens while the agent communicates empathically with stressed claimants. The AI agent automatically identifies complex cases, escalating them to expert adjusters. Meanwhile, it provides all the important details and preliminary analysis with referrals to human adjusters.
2. Flexible Claims Handling
Agentic AI solutions can tackle complex claim cases that traditional systems struggle to process. For disability income claims, AI agents collect detailed medical information and coordinate with healthcare providers to ensure accurate and comprehensive assessments. They also assess how disability affects workability and manage ongoing benefit decisions while ensuring compliance with privacy regulations. These systems detect potential fraud signs and suggest the investigation process without creating adversarial customer interactions.
3. Intelligent Policy Servicing
AI agents excel at policy modification requiring complex business rule applications. For instance, a policyholder wants to increase homeowners’ coverage. The AI agents assess property values, review risk factors, calculate premium adjustments, and manage the process. Additionally, it also explains the implications to policyholders and suggests other coverage protections that might be a good fit.
4. Underwriting Decision Support
Autonomous insurance agents help underwriters by analyzing applications, extracting relevant details from documents, and providing preliminary risk assessments with proper reasoning. For commercial general liability insurance applications, they review business descriptions, assess industry risk profiles, and identify coverage issues.
Given all these practical applications, it is evident why “2025 is the year of agentic AI.” These use cases signal a broader paradigm shift. Perhaps this is why 44% of the organizations plan to implement agentic AI within the next two years. Now, let’s look at the technologies that enable AI agents to function at this level of sophistication.
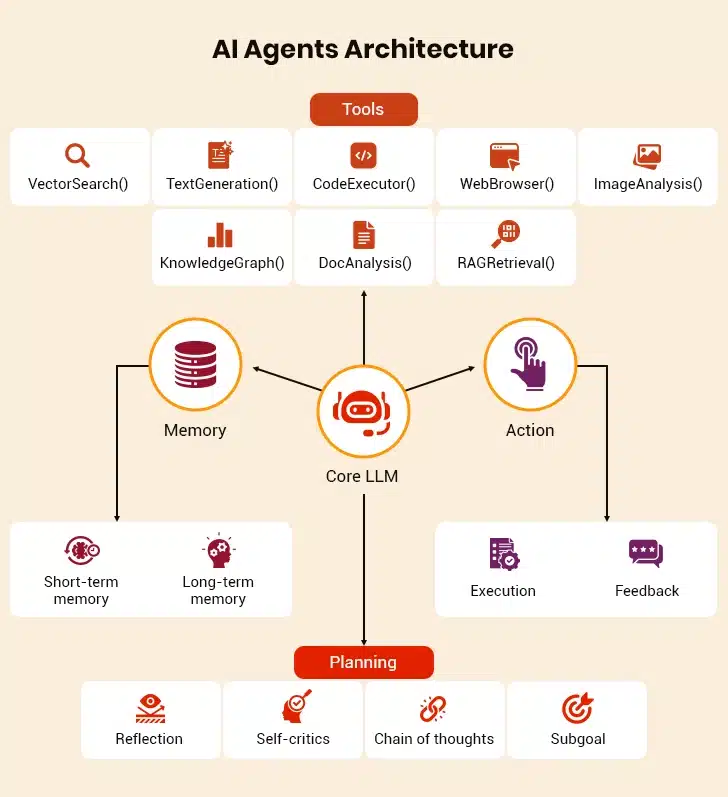
Core Components of AI Agents
The power of AI agents lies not just in their software but in the ecosystem of technologies that enable them to act, learn, and make decisions. From LLMs to real-time integration frameworks, several core enablers are behind the rise of intelligent automation in insurance. Here’s a closer look at the tech stack driving these next-gen digital workers:
I. Advanced Language Models and Insurance Context
AI agents use large language models trained on insurance terms, processes, and regulations. These models know the difference between “collision” and “comprehensive” coverage. They also understand the nuances of policy language and can interpret policyholders’ descriptions of complex loss scenarios.
For AI agents to perform aptly in insurance, the key lies in training for a specific field. This allows agents to handle insurance conversations like professionals rather than merely providing generic customer service responses.
II. Real-Time Data Integration Architecture
Insurers must verify coverage, check claim history, and access customer preferences within milliseconds to provide “instant” responses. With a real-time data integration layer, AI agents can perform such tasks exceptionally well. These layers connect policy management systems, claims platforms, and external data sources simultaneously. Unlike traditional API connections that require manual configuration for each data source, AI agents use semantic understanding to automatically interpret and synthesize information from different systems.
III. Machine Learning for Continuous Optimization
Another interesting fact that builds up the case for AI agents in insurance is their ability to improve through interaction analysis. The ML algorithms identify successful response patterns and optimize response strategies. These systems can determine which explanation style works best for different customer types and identify the steps that lead to the fastest claim solutions. The best part is that this learning occurs within set parameters that maintain compliance with regulatory requirements and company policies.
IV. Enterprise-Level Security and Compliance Framework
AI agents are equipped with built-in security controls that monitor data access, maintain audit trails, and ensure compliance. These systems can demonstrate how they made decisions for regulatory assessments while protecting sensitive customer information throughout all interactions.
With the foundation of AI agents clearly defined, the next question is, what business value does this next-gen insurance technology provide? Let’s explore how these capabilities translate into strategic gains for insurers.
Strategic Benefits for Insurers
The rise of AI agents isn’t just another technological upgrade about replacing outdated systems; it is about unlocking measurable business value. From cost savings to compliance, these agents bring efficiencies directly impacting an insurer’s bottom line. Here’s how intelligent automation reshapes the insurance value chain:
I. ROI Through Operational Efficiency
Organizations utilizing intelligent virtual assistants in insurance experience a significant reduction in routine inquiry handling costs within the first six months. Human agents can better focus on complex cases requiring empathy and specialized expertise. This enhances job satisfaction and helps deliver better customer outcomes. Furthermore, the efficiency gains multiply over time as AI agents learn from successful interactions and continuously optimize their processes.
II. Risk Mitigation and Compliance Enhancement
AI agents provide detailed interaction logs that support regulatory compliance while reducing human error risks. These systems ensure that company policies and regulatory requirements are thoroughly applied across all customer interactions. In doing so, AI agents can also identify potential issues before they become regulatory problems.
III. Scalability Without Proportional Cost Increases
Traditional customer service scaling requires linear staff additions. Thanks to AI agents, insurance companies can manage volume spikes without performance degradation. They can provide consistent service quality during natural disasters, policy renewal periods, or other peak demand scenarios.
This scalability enables insurers to maintain high service levels while controlling operational costs during unpredictable demand fluctuations. After all, these are the moments of vulnerability where a policyholder seeks support. The insurance company that performs well during such times can easily win a customer for a lifetime and carve out a unique niche in the industry.
Additionally, insurers that use AI agents to streamline processes such as SOC alert triage and invoice reconciliation can reduce manual labor by more than 60%. There’s no wonder the AI agents’ market is following an upward trajectory. Currently valued at USD 7.84 billion, it is expected to reach USD 52.62 billion by 2030 at a CAGR of 46.3%. However, realizing these benefits depends on thoughtful implementation. Let’s look at how to approach this shift strategically and responsibly.
What Frontrunners Are Doing with Gen AI in Insurance Differently
Implementation Strategy and Risk Management
Deploying AI agents in insurance isn’t plug-and-play. Instead, it requires alignment across technology, compliance, and culture. Careful planning and effective change management are necessary to ensure a smooth adoption process without disruption. Here’s a detailed look:
-
Technology Integration Approach
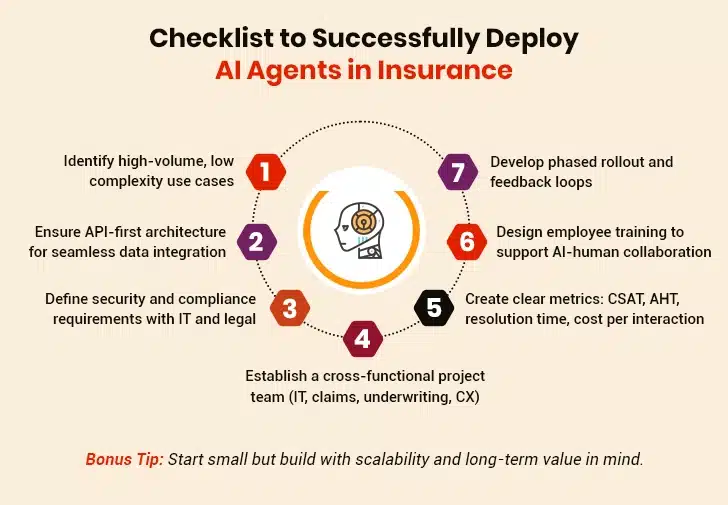
Successful AI agent deployment requires API-first integration strategies that preserve existing system functionality while enabling new capabilities. Insurance companies should prioritize integration approaches that complement current workflows rather than requiring system replacements. The implementation spans six-twelve months from pilot launch to full deployment. Herein, the initial focus is on high-volume, low-complexity use cases that demonstrate clear value.
-
Data Security and Regulatory Compliance
Implementation must address data governance requirements from project inception. AI agents require access to sensitive customer information. For this, insurers must implement strict security controls and maintain audit trails for regulatory assessments. Organizations should establish clear data access policies, implement role-based security controls, and ensure AI decision-making processes remain explainable for compliance purposes.
-
Change Management and Employee Adaptation
Stakeholders should remember that success depends on positioning AI agents as employee enablement tools rather than replacement technologies. Therefore, training programs should foster collaboration between human professionals and AI systems. These should focus on how agents enhance productivity and simplify workflows, rather than eliminating human expertise. Employee feedback during pilot programs provides valuable insights for system optimization and change management strategy refinement.
-
Pilot Program Selection and Success Metrics
Initial implementations should target use cases with manageable complexity and provide clear value. Policy servicing for routine changes or simple property claim FNOL processes provides proof of concept while building organizational confidence. Success metrics shouldn’t be limited to purely technical performance indicators. These should also include customer satisfaction scores, resolution time improvements, and cost-per-interaction reductions.
AI is reshaping insurance—stay ahead with DAMCO’s smart solutions!
Wrapping Up
The transition from traditional chatbots to AI agents is a strategic move for insurance companies. It goes beyond simple insurance automation to transform fundamental operations, positioning insurers for sustained competitive advantage. Leaders who recognize this opportunity can establish market differentiation by delivering superior customer experiences and achieving operational efficiency.






