Netflix knows what movie you’ll watch next. Google anticipates your questions before you finish typing. Amazon predicts what you’ll buy. These companies use data mining to unearth patterns in human behavior. Now imagine applying that same predictive technology to save lives!
The algorithms behind movie recommendations can be adapted to forecast heart attacks. Much like suggesting products, these algorithmic systems can also identify patients at risk of heart attacks or other complications. This is the power of data mining in healthcare, digging up insights that can transform how diseases are predicted, prevented, and treated.
Table of Contents
The numbers tell a striking story. The global big data in healthcare market size is estimated to grow to USD 540 billion by 2035 from USD 78 billion in 2024, with a CAGR of 19.20%. Even more remarkable, the global healthcare analytics market size is currently valued at USD 64.49 billion. It is predicted to touch the USD 369.66 billion mark by 2034, representing a healthy CAGR of 21.41%. This represents a remarkable leap, indicating the exponential growth of the sector.
Yet there’s a problem. Despite the exponential growth in health data, a significant amount of it remains unused. Every day, hospitals collect millions of records. Patient monitoring systems generate endless streams of data. Lab results pile up in digital warehouses. Healthcare faces a crisis. Costs spiral up. Patients demand better care. Doctors feel overwhelmed by information. Traditional methods cannot handle the complexity of modern medicine. Thus, the solution lies in adopting data mining healthcare solutions that can unlock patterns hidden in medical data.
What is Data Mining in Healthcare?
Data mining is the process of sifting through large datasets to discover hidden patterns and relationships. This unlocks a new plane of insights that might otherwise go untapped with basic data analytics.
“We are surrounded by data but starved for insights.” Jay Baer, Global Business Strategist and Serial Entrepreneur
Think of healthcare data as a large warehouse containing medical records, patient diagnoses, test results, treatment plans, genomic data, and more. Data mining in the healthcare industry is akin to a team of highly skilled investigators who utilize advanced algorithms to sift through information to extract actionable insights. Such an in-depth analysis reveals:
- Trends and patterns in disease progression, which allow healthcare providers to intervene during the early stages to improve treatment efficacy and patient outcomes.
- Opportunities for early disease detection and prevention by correlating patient profiles with associated risk factors to compute the possibility of developing certain illnesses.
- Effectiveness of treatment in certain patient groups to understand which treatments are most effective and appropriate for certain patient demographics.
- Potentially harmful drug interactions to prevent adverse drug reactions and improve patient safety and well-being.
- Trends in resource utilization, patient admissions, etc., for effective resource optimization for continued care.
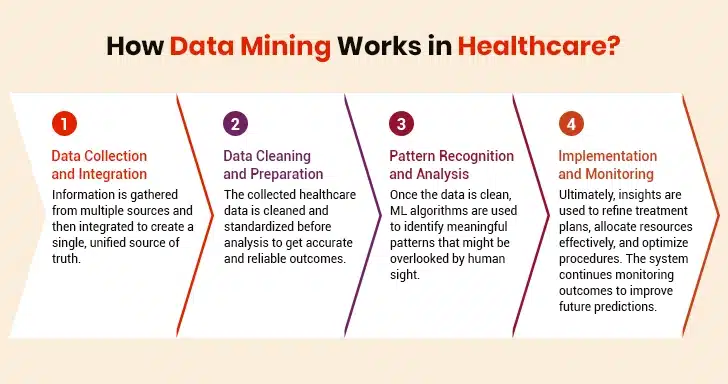
It is quite evident why data mining is important in healthcare. To sum up, insights gained from data mining enable healthcare institutions to optimize their operations and enhance patient outcomes. Above all, these insights empower healthcare practitioners and medical researchers to move from guesswork to precision. Thus, they can easily predict, prevent, and treat diseases with unparalleled accuracy. Now, let’s take a look at how data mining in healthcare works.
Applications of Data Mining in Healthcare: A Cure for Many Ailments
From personalizing patient care to detecting fraud in health insurance claims, data mining can comfortably fit across various healthcare and allied activities. To illustrate this point, here are some common data mining applications in healthcare:
- 1. Personalized Medicine: Data mining in healthcare involves analyzing patient data, such as medical history, genetic makeup, lifestyle, etc., to tailor treatment plans. By aligning treatment with individual needs, healthcare institutions can deliver more effective care with improved patient outcomes.
- 2. Preventive Care: Data mining lays the foundation for predictive analytics, which enable healthcare institutions to identify the likelihood of an individual developing certain diseases. Such foresight allows for early intervention and preventive care that mitigates the impact of illnesses, if not wards it off entirely.
- 3. Chronic Disease Management: When it comes to chronic disease management, data mining helps monitor health levels and predict complications. Such a proactive and vigilant approach to care prevents complications or hospitalization while reducing the burden on healthcare infrastructure.
- 4. Clinical Research and Drug Discovery: Researchers use advanced data mining tools to dig deeper into the vast data reserves of medical records, studies, clinical trials, etc. This helps them identify promising areas of R&D while developing new drugs and treatment plans.
- 5. Hospitalization Management: Effective data mining helps identify patients at risk of hospitalization and readmissions. These can be prevented through early-stage intervention and continued care, resulting in lower overall healthcare costs for patients.
- 6. Mass Healthcare: By mining through data on population health, establishments can identify trends surrounding pandemics, disease prevalence, risk factors, etc. This information helps develop targeted public healthcare programs and initiatives to support and improve population health.
- 7. Remote Patient Monitoring: The data collected from smart wearable devices and other remote monitoring tools can widen the scope of data mining in healthcare industry. Such accessibility to first-party data allows healthcare providers to track health in real time and execute interventions in case of concerns.
The applications of data mining in healthcare are vast and varied, from remote patient monitoring and clinical research discovery to preventive care and chronic disease management. In addition to these applications, effective data mining offers a plethora of advantages, all of which are too significant to ignore. Let’s explore them in detail.
How Data Mining Enhances Customer Targeting for Businesses
Benefits of Data Mining in Healthcare
The advantages of healthcare data mining extend far beyond simple cost savings and efficiency improvements. These advantages create a cascade of positive effects, transforming how healthcare organizations operate, and patients experience care. Here’s an overview of the benefits of data mining in healthcare:
- I. Enhanced patient care through targeted treatment delivery, personalized medicine, improved disease prevention, early detection and intervention, etc. .
- II. Optimized resource allocation and utilization in healthcare establishments based on in-patient admissions trends and other medical care-related activities.
- III. Reduced healthcare costs through early disease detection, preventive care, and optimized resource allocation.
- IV. Advanced research and development of innovative drugs and treatment plans. Researchers can use it to identify promising areas of healthcare.
- V. More effective patient care and data-driven decision-making for informed diagnoses, treatment plans, and patient care.
- VI. Protection from fraud and abuse, and corresponding financial losses, by flagging anomalous patterns.
Given these benefits, the importance of data mining in the healthcare industry is self-explanatory. However, the process is not without its challenges. These issues prevent healthcare institutions and decision-makers from harnessing the full potential of data. Thus, these must be addressed immediately.
Challenges of Data Mining in Healthcare: Possible Roadblocks with Solutions
While the applications and advantages of data mining in healthcare are attractive, it is not immune to obstacles either. Here are some challenges of data mining in healthcare, along with possible solutions:
- a. Data Quality and Standardization: The vast amounts of healthcare data is spread across systems, organizations, and departments. Thus, it becomes siloed, obsolete, inconsistent, and riddled with errors, failing to provide a comprehensive view. Institutions can combat it by implementing data quality standards and enforcing strict data governance practices that ensure consistency and accuracy.
- b. Data Privacy and Security: Medical and healthcare data is highly personal, making data privacy and security paramount. Even the smallest of data breaches can have catastrophic effects. To mitigate this, institutions must avail data mining services that employ robust data security measures like anonymization and encryption to mask sensitive information. At the same time, prioritizing patient consent and maintaining transparency regarding data collection and use will also cultivate trust.
- c. Algorithmic Bias: Data mining can perpetuate and reinforce biases existing in healthcare data. This could result in inaccurate and unfair results. In some cases, it might gloss over an entire demographic that is often underrepresented in healthcare data. To prevent this, develop and utilize diverse training datasets to restrict bias. Pair this with human oversight in decision-making. Conduct regular audits and update algorithms to ensure fairness.
- d. System localization: Healthcare organizations often employ proprietary systems. Such digital ecosystems limit interoperability, hinder collaboration, and restrict data sharing. Investing in interoperable data platforms that facilitate data exchanges while maintaining security prove useful in the long run. If not for a system overhaul, integrations can also help in setting up comprehensive networks.
By carefully addressing the challenges, healthcare providers and researchers can make the most of medical data. And, having covered the process, its applications, benefits, considerations, and challenges, let’s explore what the future holds for healthcare data mining.
The Future of Data Mining in Healthcare
The healthcare industry stands at the threshold of a technological revolution. Emerging technologies and evolving capabilities will dramatically expand the possibilities for data mining in healthcare over the next decade.
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration
Artificial intelligence represents the next frontier in healthcare data mining. Modern AI systems can process vastly more complex data than traditional statistical methods. They can analyze medical images, interpret natural language, and identify subtle patterns that human analysts might miss.
Machine learning algorithms continuously improve their performance as they process more data. This self-improving capability means that healthcare data mining systems will become more accurate and valuable over time. For instance, NLP-powered data mining tools can analyze doctor notes, research papers, and patient communications. These sources of information were previously difficult to analyze.
Machine Learning vs Data Mining: Key Differences & Similarities
“The convergence of AI and healthcare data creates unprecedented opportunities to transform patient care, but success requires careful attention to clinical validation and ethical implementation.” Dr. Regina Barzilay, Pioneer in Healthcare AI, MIT
2. Real-Time Analytics and Edge Computing
Real-time insights are imperative for the healthcare industry. Traditional data mining approaches often fail to meet these time-sensitive requirements. These are necessary to enable continuous patient monitoring and early warning systems. Wearable devices and remote monitoring systems generate continuous streams of health data.
Real-time analytics can process this information to provide ongoing health insights and early intervention opportunities. Edge computing brings analytical capabilities closer to the point of care. Medical devices, monitors, and sensors can perform local analysis and provide immediate alerts when problems are detected.
3. Genomic Data Integration
Genomic medicine represents one of the most promising applications of advanced data mining techniques. As genetic testing becomes more affordable and accessible, healthcare organizations will need to integrate genomic data with traditional clinical information.
Pharmacogenomics uses genetic information to predict drug responses and optimize medication selection. This approach can reduce adverse drug reactions and improve treatment effectiveness. Precision oncology analyzes tumor genetics to identify optimal cancer treatments. This approach has already shown remarkable success in treating certain types of cancer and will likely expand to other areas of medicine.
Population genetics studies can identify disease risk factors and develop prevention strategies. These insights inform public health policies and individual risk assessments.
Conclusion
Data mining is a powerful tool possessing the potential to revolutionize healthcare. It makes healthcare data-driven to improve patient outcomes in multivariate ways while also managing the load on healthcare institutions. However, to extract the benefits of data mining in healthcare, institutions have to address concerns surrounding data quality, privacy, algorithmic bias, and system localization. To sum up, data mining is a step towards making healthcare healthier!