The promise of increased agility, reduced costs, enhanced security, improved performance, and faster time to delivery has lured enterprises to migrate workloads and applications to the Azure Cloud. However, the journey to successful on-premises to Azure cloud migration is not without its challenges. In fact, migrating virtual machines, on-site hardware, databases, VMware, apps, and storage to the cloud can be overwhelming. Statistics reveal that a staggering 70% of enterprise cloud migrations fail and only 25% of organizations meet their migration deadlines. This is where the need for best practices comes in to minimize disruptions, mitigate risks, and harness the benefits of Azure cloud migration.
“Treat cloud migration as a business transformation, not just an IT project.”
– Julia White, Corporate Vice President, Microsoft Azure.
Table of Contents
What Are the Best Practices for Azure Cloud Migration?
What Are the Key Challenges of Azure Cloud Migration?
What Are the Popular Migration Strategies for Azure Cloud?
What Are Common Ways to Measure the Success of Azure Cloud Migration?
What Are the Best Practices for Azure Cloud Migration?
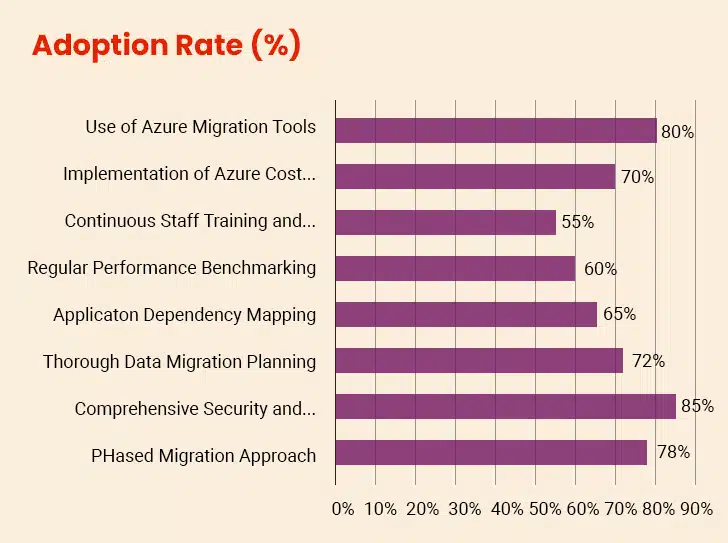
Moving to the Azure cloud works best when done carefully. Given below are the Azure cloud migration best practices guiding companies through preparing systems, moving data safely, and adjusting to the cloud environment.
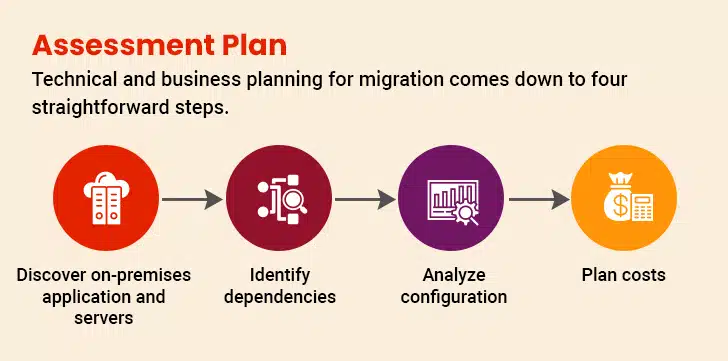
1. Comprehensive Planning
Comprehensive planning lays the groundwork for smooth cloud migration, minimizing disruptions and optimizing the utilization of Azure database migration. Begin with a meticulous and detailed assessment of the organization’s existing infrastructure, applications, and workloads to form a clear understanding of dependencies and requirements. This will help in developing a clear migration strategy that goes beyond basic cloud-native tools and entails a strategic approach that ensures the migration process is aligned with the broader objectives of the organization. In a nutshell, a well-defined roadmap not only sets the stage for a frictionless migration but also helps in the identification of potential challenges that come along the way.
Key Considerations to Take in Account for Cloud Migration
2. Prioritize Security
Adopting a “security first” approach is crucial when migrating assets from on-premises to the cloud. This practice entails safeguarding sensitive data by prioritizing security considerations at every stage of the cloud migration process. By utilizing Azure Active Directory, organizations can implement robust identity and access management practices ensuring that only authorized users can access resources.This in turn, minimizes the risk of unauthorized breaches. Furthermore, employing Azure Key Vault allows organizations to encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest for secure key management. Besides safeguarding sensitive data, adherence to industry-specific regulations and compliance standards ensures that migration to Azure Cloud aligns with legal requirements. By prioritizing security, organizations can lay a robust foundation for their cloud environment and instill confidence in stakeholders, fostering a secure and compliant digital landscape.
3. Data Assessment and Classification
Data assessment and classification is a critical step for a smooth and secure transition to the Azure cloud environment. This practice entails a meticulous analysis of an organization’s data to understand its importance, characteristics, sensitivity, and potential risks. By conducting a detailed examination, organizations can classify data based on criticality and regulatory requirements. This sets the stage for developing a robust migration strategy, enabling organizations to implement appropriate security measures. Furthermore, the process involves a data cleansing process to improve accuracy, enhance efficiency, and reduce the risk of errors while maintaining the integrity of the data being migrated.
4. Choose the Right Azure Services
Choosing the right Azure services is pivotal for the success of cloud migration endeavors. When assessing the requirements based on an organization’s workloads and applications, it’s important to consider factors such as performance, scalability, and integration capabilities. This practice emphasizes a tailored migration approach, allowing organizations to optimize their usage of Azure cloud resources and build a resilient and scalable infrastructure that meets both existing and future demands. In a nutshell, selecting the right Azure services allows organizations to enhance their capabilities and unlocks the full potential of the cloud while experiencing a hassle-free migration.
Is Cloud Migration the Ultimate Solution for Reviving Legacy Applications
5. Pilot Testing
Pilot testing is another pivotal practice that allows organizations to validate and refine their Azure cloud migration strategies before going for full-scale implementation. This phase entails choosing a subset of workloads or applications for cloud migration to identify and mitigate potential challenges. By involving end-users in the testing process, organizations can ensure that migrated applications meet functionality, usability, and performance expectations. The insights gleaned from pilot testing can play a crucial role in decision-making such as the identification of potential issues, adjustments to the existing plan, and validation of the selected cloud migration approach.
6. Performance Monitoring
Performance monitoring is a common migration practice that entails the implementation of robust monitoring tools such as Azure Application Insights and Azure Monitor,These tools provide real-time insights into application performance, resource utilization, and overall system health. This helps optimize resource allocation, identify and address bottlenecks, and ensure that workloads and applications meet desired performance levels. In other words, this iterative process of performance monitoring allows organizations to proactively manage their Azure cloud resources and ensure that migrated applications function at their optimal efficiency. It also delivers the desired benefits of responsiveness, reliability, and scalability in the Azure cloud environment.
7. Backup and Disaster Recovery
Backup and disaster recovery are crucial when considering cloud migration to safeguard sensitive data and ensure business continuity during unexpected outages. This practice entails establishing comprehensive backup strategies using Azure Backup. Furthermore, organizations can utilize Azure Site Recovery to create a robust disaster recovery plan that allows quick recovery of applications or services in unforeseen events.
Ensure Business Continuity With a Cloud Disaster Recovery Plan
8. Post-Migration Evaluation
This cloud migration practice entails a thorough assessment to evaluate the performance of migrated workloads and applications, the realization of predefined goals, and the overall impact on business operations. Through this assessment, organizations can gain insights into areas for improvement and optimization.
What Are the Key Challenges of Azure Cloud Migration?
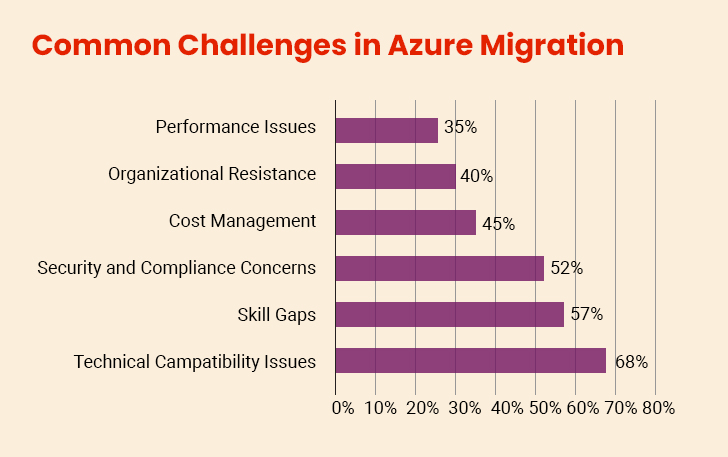
Cloud migration to Azure presents real obstacles. From data transfers to cost control, companies often struggle with predictable issues. The good news? Every challenge has practical solutions that help complete the transition successfully.
I. Lack of Skilled Team Members
Moving to Azure requires special skills that many companies don’t have in their teams. Many DevOps and cloud engineering teams struggle with the technical knowledge needed for successful migration. Companies often find themselves stuck because their current IT staff doesn’t understand how Azure works or how to move applications safely. This creates delays and increases the risk of making costly mistakes during the migration process.
Solution
Get proper training for your team or hire experts who know Azure well. Consider working with Azure partners who can guide you through the process and teach your staff along the way.
“Your Azure skills gap will derail migration faster than any technical issue.”
– Donovan Brown, Former Partner Program Manager, Microsoft.
II. Security and Data Protection Issues
Moving your business data to the Azure cloud brings new security worries that many companies struggle with. Your sensitive information needs protection from unauthorized access. Companies often worry about losing control over their data when it moves from local servers to the Azure cloud platform. There are also concerns about meeting legal requirements and industry rules that govern how data should be stored and handled.
Solution
Use Azure security tools like Security Center and Active Directory to protect your data. You may also set up proper access controls and regular security checks to protect your data.
III. Poor Planning and Unclear Goals
One of the most common pitfalls is migrating to Azure without clear objectives. Companies often rush into migration without understanding what they want to achieve or how much it will cost. This leads to confusion about which applications to move first and how to measure success. Without a proper plan, the migration process becomes chaotic and expensive.
Solution
Create a detailed migration plan with clear goals and timelines. Start with small, simple applications before moving to larger systems. Define what success looks like for your business.
IV. Unexpected Costs and Budget Problems
Moving to Azure can become much more expensive than companies expect if they don’t understand how cloud pricing works. Many businesses forget about ongoing costs like data storage, network usage, and support services. They also don’t realize that some applications might need expensive changes to work properly in Azure. This leads to budget surprises that can hurt the business financially.
Solution
Study Azure pricing carefully and use cost calculators to estimate expenses. Monitor your spending regularly and set up alerts when costs get too high. Plan for extra expenses during the migration period.
“Azure cost optimization begins on Day 1; not after the bill arrives.”
– Sarah Lean, Senior Cloud & AI Infrastructure Solution Engineer, Microsoft.
V. Data Migration Complexity
When you are migrating large volumes of data, it can be a time-consuming, complex experience. Data loss can occur due to various reasons, such as human error, technical malfunction, or cyberattacks. Moving large amounts of data from old systems to Azure takes time and careful planning. Companies often underestimate how long this process will take and the technical challenges involved.
Solution
Break down data migration into smaller chunks and test each part meticulously. Use data migration tools and services offered by Azure. Also, backup your data before starting the migration process.
VI. Application Compatibility Problems
Not all applications work well in Azure without changes. Some older programs might need expensive updates or complete rewrites to function properly in the cloud. Companies often discover these compatibility issues too late in the process, causing delays and additional costs. This is especially challenging for businesses with custom-built software or legacy systems.
Solution
Test all applications in Azure before the full migration. Identify which programs need updates and plan for the time and money required to make these changes.
VII. Resistance to Change from Employees
Many employees feel scared when companies decide to move their systems to the Azure cloud. They think the new system will make their jobs harder, or they might lose their jobs completely. This resistance can slow down the migration process and make it harder to get the full benefits of moving to Azure.
Solution
Communicate clearly about the benefits of Azure migration. Provide training and support to help employees adapt to new systems. Involve key team members in the planning process to build support.
Discover How a Tech Company Migrates Inventory Management Platform to Azure Cloud
What Are the Popular Migration Strategies for Azure Cloud?
Moving to the Azure cloud can be done in different ways. Given below are the popular strategies that help businesses choose how to shift their systems. Some strategies move systems quickly with few changes, while others take longer but improve applications significantly.
| Migration Strategy | Description | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
| Rehost | Move applications and workloads to Azure without significant changes. | Quick migration, minimal changes, legacy apps. |
| Refactor | Make minimal changes to optimize applications for the cloud without a full redesign. | Improve performance/cost efficiency with moderate effort. |
| Rebuild | Redevelop applications from scratch using cloud-native technologies. | When legacy apps are outdated or require full modernization. |
| Replatform | Similar to rehost, but with some optimizations for the cloud environment. | When slight improvements are needed without a full refactor. |
| Repurchase | Replace existing applications with SaaS or cloud-native alternatives. | When better cloud solutions are readily available. |
| Retain | Keep some applications on-premises temporarily or permanently. | When migration is not feasible or necessary. |
| Retire | Decommission applications that are no longer needed. | To reduce complexity and costs. |
How an Animal Health Distributor Boosts CSAT with a Data Engineering Solution powered by Azure
What Are Common Ways to Measure the Success of Azure Cloud Migration?
Measuring migration success goes beyond technical checks. Given below are the key indicators to measure Azure cloud migration success.
1. Cost Savings Analysis
One of the main reasons companies move to Azure is to save money. You can measure success by comparing how much you spent on your old computer systems with what you pay for Azure services. This includes analyzing server costs, electricity bills, and money spent on maintaining equipment. When you see reduced spending on hardware, you know the migration is working well for your budget.
2. Performance Monitoring
After moving to Azure, you need to check the performance of your applications and websites. This means analyzing how quickly pages load, how fast data gets processed, and whether users can access everything without delays. Good performance means your systems are working better in the cloud. Whereas slow performance might mean you need to make some tweaks to get the optimum results.
3. Downtime Tracking
Downtime happens when your systems stop working, and users cannot access the applications or data. Measuring success means tracking how often this happens and for how long. A successful migration should result in less downtime compared to your old setup. When your systems stay online more often and recover quickly from problems, it shows that Azure offers better reliability than your previous infrastructure.
4. User Satisfaction Surveys
The people who use your systems every day are the best judges of whether the migration worked well. You can ask them about their experience through simple surveys or feedback forms. Questions about system speed, ease of use, and overall satisfaction help you understand if the migration made things better for users. Happy users usually mean migration has improved their daily work experience.
5. Scalability Testing
Scalability means your systems can handle more users when needed. You can test this by gradually increasing the load on your Azure systems and analyzing how they respond. A successful migration should allow you to easily add more resources when busy periods come. When your systems can grow and shrink based on demand without problems, it shows Azure is working as expected.
6. Backup and Recovery Success
Having good backups means you can get your data back if something goes wrong. You should test your backup systems regularly to make sure they work properly. A successful migration includes having faster and more reliable ways to restore your information compared to your old setup. When you can quickly recover from data loss or system failures, it proves that Azure is providing better protection for your business.
7. Compliance and Reporting
Many businesses need to follow specific rules about how they handle data and run their systems. You can measure success by checking if Azure helps you meet these requirements more easily than before. This includes generating reports that show you are following the rules and maintaining proper records. When compliance becomes easier and you can produce required reports quickly, it shows that the migration has improved your ability to meet legal and business requirements.
Drive Business Impact with Damco’s Expertise
As organizations embark on their Azure cloud migration journey, it becomes imperative to note that success lies not merely in the technicalities of moving applications but in the meticulous execution of a holistic strategy. From comprehensive planning to post-migration evaluation, each best practice plays a vital role in a smooth transition. If you are also planning to migrate assets from on-premises to the cloud, you may follow the best practices aforementioned in this insightful post or seek help from a reliable cloud migration partner like Damco.