Blockchain comes with the ability to redefine the way users store data or make transactions. This technology has been making strong waves for a unique feature. Do you know what it is? It is immutability. It means data once recorded in a Blockchain won’t be changed or deleted, providing users with a high level of security. This makes Blockchain a powerful tool against fraud.
“Immutable records eliminate ‘he said, she said’ disputes in business contracts.”
– David Chaum, Founder, Elixxir.
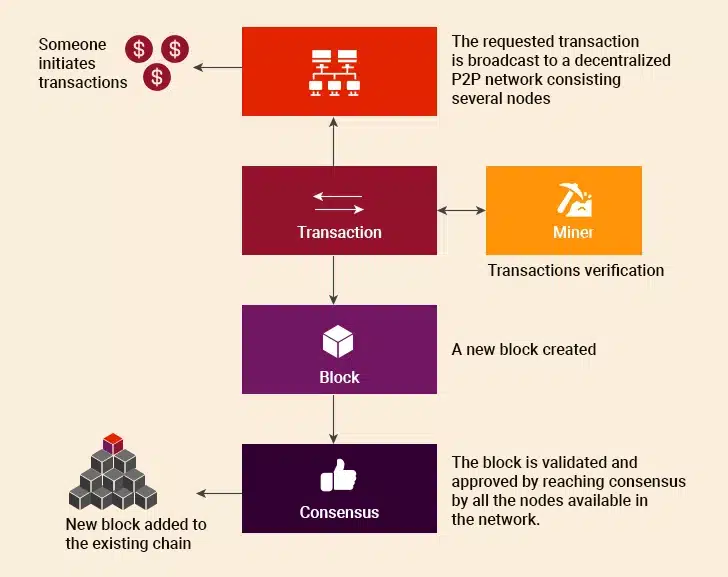
Fraud is a serious concern in many data-intensive industries. When records are easily altered, it opens the door for miscreants to exploit data. This leads to huge financial losses for businesses that deal with data. However, with Blockchain’s digital ledger, it becomes much harder to commit fraud. But how does Blockchain prevent fraud? Let’s try to understand. Each block in the chain holds a record of data. When a new block is added, it connects to the previous block using special codes. This creates a chain that is hard to alter. If someone tries to change a record in one block, it will change all the blocks after it. The network would notice this and reject the fraud.
This insightful post explores the types of fraud prevention with Blockchain technology. It also discusses the benefits and key features of Blockchain’s irreversible nature. Lastly, it explores the future of immutability in fraud prevention.
Table of Contents
How Does Blockchain Technology Help in Combating Different Types of Fraud?
What are the Blockchain Immutability Benefits?
- 1. Increased Trust Among Users
- 2. Automated Blockchain Fraud Detection
- 3. Reduced Risk of Human Error
- 4. Easy Tracking and Auditing
- 5. Enhanced Data Security
What are the Key Features of Blockchain Immutability?
What is the Future of Immutability in Blockchain Fraud Prevention?
How Does Blockchain Technology Help in Combating Different Types of Fraud?
Blockchain fights fraud in smart ways. Explore how this technology makes cheating nearly impossible by creating systems where every transaction is permanent, visible to all, and verified by multiple parties.
| Type of Fraud | How it Occurs | How Blockchain Immutability Helps |
|---|---|---|
| Identity Theft | This happens when someone uses another person’s data without permission. For example, a miscreant uses stolen data to create fake accounts. | Blockchain securely stores and verifies user identities using cryptographic techniques. Once identity data is recorded, it won’t be changed or deleted. This makes it tricky for thieves to steal personal information. |
| Payment Fraud | This involves unauthorized payments. For example, a criminal steals the payment details of users and makes purchases without permission. | Blockchain keeps an unchangeable record of all transactions. This allows real-time monitoring of financial activities to spot any unusual transactions or activities. |
| Credit Card Fraud | This happens when someone uses credit card information to make transactions. For example, a stolen card is used without permission. | Blockchain provides a permanent record of all transactions. This makes it easier to trace the origin of any suspicious activity. |
| Illegal Gains | This involves hiding the details of illegally gained money, usually through complicated transfers. For example, using cryptocurrency to hide the source of illegal money. | The open nature of Blockchain allows authorities to follow the money trail. This helps identify any suspicious transactions. |
| Supply Chain Fraud | This happens when product information is changed or faked in the supply chain. For example, fake goods are sold as real products because there is no clear way to track them. | Blockchain tracks goods as they move through the supply chain. This irrevocable tracking ensures products are real and haven’t been changed, preventing counterfeit goods. |
| Insurance Fraud | This happens when someone makes false claims to get money or benefits. For example, submitting a fake claim for a lost item that never existed, using forged documents. | Smart Contracts on Blockchain automatically process and verify insurance claims. This helps reduce fake claims by making sure all requirements are met before payouts. |
| Cryptocurrency Fraud | This involves scams with digital currencies, like Ponzi schemes. For example, promising high returns on investments in a fake cryptocurrency project. | Blockchain uses a hashing process to provide an unchangeable audit trail for investigating and identifying fraudulent schemes. |
Use Cases of Blockchain Technology Across Industries
What are the Blockchain Immutability Benefits?
Immutability makes Blockchain uniquely useful. Given below are the benefits highlighting how immutability creates trust, prevents fraud, and keeps past records intact. This makes systems more reliable for everything from money transfers to supply chain tracking.
1. Increased Trust Among Users
The unchangeable nature of Blockchain builds trust among users. When people know the information won’t be changed or tampered with, they feel more confident using the system. This trust is very important in financial transactions, where users need to know that their money and data are safe. By providing a secure space where every transaction is visible and permanent, Blockchain encourages more people to take part in digital transactions. This trust benefits individual users and makes the system stronger, making it harder for fraudsters to succeed.
2. Automated Blockchain Fraud Detection
Blockchain also helps in fraud detection. With Smart Contracts, which are agreements written into the Blockchain, businesses set specific rules for transactions. If a transaction doesn’t follow these rules, the Smart Contract automatically marks it as suspicious. This quick response helps detect potential fraud before it causes problems. By using Blockchain technology to monitor transactions all the time, businesses act fast if something unusual happens, making it much harder for fraud to go unnoticed. This proactive way of detecting fraud increases security and protects users from financial losses.
3. Reduced Risk of Human Error
Blockchain also lowers the chances of human mistakes. In regular systems, people might accidentally change or delete important information. This allows criminals to manipulate data. However, in Blockchain, data once recorded won’t be changed or deleted. This means that there is no risk of accidental mistakes. This reliability means everyone trusts that they are using the right information. By reducing mistakes, businesses focus on their primary goals without worrying about data integrity. This helps prevent fraud caused by human errors.
4. Easy Tracking and Auditing
Another benefit of Blockchain’s unchangeable nature is that it makes it easy to track and audit transactions. This raises an important question: how does Blockchain ensure data immutability and transparency? The answer lies in its permanent record-keeping. Since all transactions are recorded permanently, anyone can look back and see the full history of a transaction. This is helpful for businesses that need to show their transactions are legitimate. If fraud happens, the record helps investigators quickly find out what went wrong and who was involved. This transparency helps prevent fraud because it makes criminals think twice before doing anything wrong.
5. Enhanced Data Security
The irreversible nature of Blockchain makes data much safer. This means once a transaction occurs, it won’t be changed or deleted and will stay there forever. For example, if someone tries to change a transaction to steal money, the original record will remain on the network, making it easy to detect fraud. This helps users and businesses trust that their data is safe.
How Blockchain App Development Paves the Way for the Future
What are the Key Features of Blockchain Immutability?
The immutable nature of Blockchain has special qualities. Given below are the features that show how the technology prevents alterations to past records while allowing new additions that stay accurate and verifiable forever.
I. Permanent Data Storage
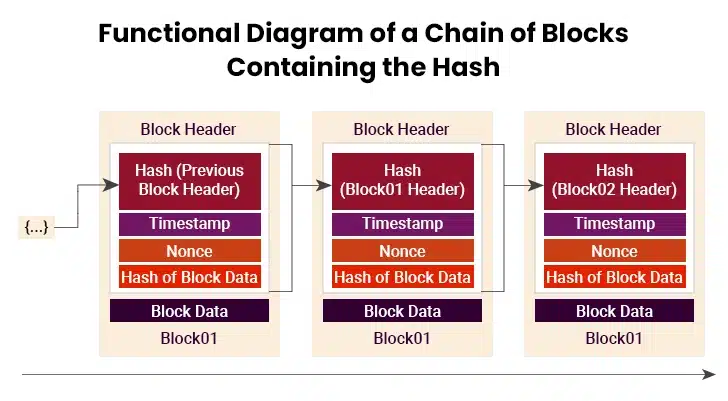
Immutability means the ability for a Blockchain ledger to retain a permanent and unchangeable history of transactions. Once information gets added to the Blockchain network, it stays there forever and cannot be removed or changed. This creates a complete record of everything that has happened since Blockchain started working. The data becomes part of the chain structure and gets protected by special computer codes that make it nearly impossible to alter. This permanent storage helps people trust the system because they know the information will always be there exactly as it was first recorded.
II. Cryptographic Hash Protection
Cryptographic hashing is key to Blockchain immutability, and the most common hash function is SHA-256. Each block in the Blockchain network gets a unique fingerprint called a hash that connects it to other blocks in the chain. When someone tries to change any information in a block, the hash changes completely and breaks the connection with other blocks. This makes it obvious that someone has tried to tamper with the data. The hash system works like a security seal that shows if anyone has opened or changed the contents of each block.
III. Decentralized Network Verification
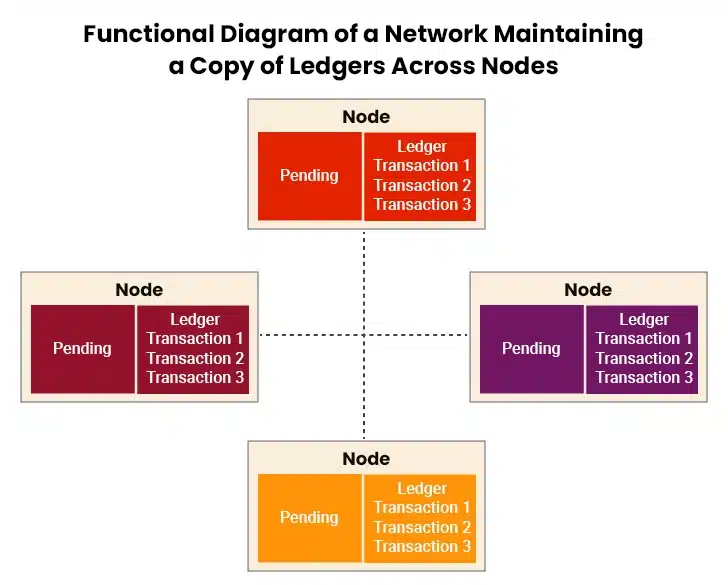
Decentralized Blockchains are unchangeable, which means that the data is irreversible once added. Instead of having one central authority checking the data, thousands of computers around the world work together to verify and protect the data. Each computer has a copy of the entire Blockchain network and checks that all the information matches with everyone else. If someone tries to alter information on one computer, all the other computers will refuse it since it does not match their records. This network of computers makes it extremely difficult for anyone to successfully change or manipulate data.
IV. Transparent Change Detection
Once a Blockchain network records data, it cannot alter or delete it without a permanent and visible record of the change. Even if someone could somehow modify the Blockchain, everyone would be able to see exactly what was changed and when it happened. The system keeps track of every single change attempt and makes this information visible to all users. This transparency means that any suspicious activity gets noticed immediately by the network participants. People can always check the complete history of any piece of data to make sure it has not been tampered with.
V. Consensus Mechanism Protection
The Blockchain network uses special rules called consensus mechanisms to decide what information is valid and what should be rejected. Before any new data gets added to the Blockchain, most of the computers in the network must agree that it is correct and follows the rules. This agreement process happens automatically and prevents fraudsters from adding false information to the chain. The consensus system also makes sure that once data is accepted and added to the Blockchain, it cannot be removed or changed later without getting approval from most of the network participants.
VI. Timestamped Transaction Records
Every piece of information that gets added to the Blockchain network includes a timestamp that shows exactly when it was recorded. These timestamps create a chronological order that cannot be changed or rearranged later. The timing information becomes part of the permanent record and helps prove when specific events happened. This feature is especially important for legal and business purposes where the exact timing of transactions and agreements matters. The timestamps work together with the other security features to create a complete and unchangeable history of all activities on the Blockchain.
What is the Future of Immutability in Blockchain Fraud Prevention?
Immutability will play a big role in preventing fraud in the future. As more industries move online, fraudsters find new ways to cheat systems. However, immutability will make it harder by locking data in a way that no one can alter. In the coming years, AI could work with Blockchain to detect fraud faster by analyzing unchangeable data logs. As trust in digital systems grows, these unchangeable record systems could become the standard for keeping data safe and secure.
Drive Business Impact with Damco’s Expertise
The irreversible nature of Blockchain makes it a powerful tool in the fight against fraud. By ensuring that data once recorded won’t be changed or deleted, this technology creates a secure environment for record-keeping and transactions. This feature not only protects sensitive information but also builds trust among users. If you are planning to use Blockchain for fraud identification, you may seek help from a reliable Blockchain partner like Damco.