Application maintenance has shifted from a routine IT task to a critical business consideration. Companies now spend a big part of their development budget on maintenance, yet they see poor returns. Costs keep rising, and IT teams face growing skill shortages.
Maintenance costs clearly require rethinking. Traditional maintenance treats applications as finished projects, not evolving assets. This creates inefficiencies that waste resources and impede value creation. A fresh approach to maintenance can transform this expense into a powerful tool for growth.
This blog explores how enterprises can turn application maintenance from a cost burden into a competitive advantage. Let us dive right in.
Table of Contents
Why Is It Time to Rethink Software Application Support and Maintenance Strategy?
What Does It Mean to Shift from Projects to Programs in Application Maintenance?
How Much Does It Cost to Maintain an Application Today?
What Are the Factors That Influence the Cost of Maintaining an Application?
How Can Enterprises Manage Application Maintenance Costs Strategically?
Why Is It Time to Rethink Software Application Support and Maintenance Strategy?
Application support and maintenance do not work the way enterprises need them to. Most organizations still follow vendor-dictated upgrade cycles and maintenance schedules that prioritize profit over value addition. This creates an imbalanced relationship where teams struggle to keep pace with their software providers.
Many IT leaders feel stuck with their software support options. They are forced to upgrade based on vendor schedules, even when those plans conflict with their organizational goals and operational needs.
Modern enterprises face tremendous pressure from every direction. The shift to remote work has changed how companies operate. It has made them push transformation faster than they originally planned. Now, IT teams must achieve more with smaller budgets. This has created an urgent need to cut costs without sacrificing performance.
Companies generally treat application software maintenance as low-priority work. No one pays attention to it until a system fails. This reactive approach puts businesses at risk. It also fails to protect vital technology investments.
Furthermore, maintenance involves a lot more than bug fixes. Technical debt builds up in every system as security flaws appear, frameworks age, dependencies become outdated, and performance deteriorates. When teams ignore regular maintenance, minor issues turn into major problems.
The business environment is never static. Over time, organizational needs change, user expectations evolve, and new opportunities come up. Companies need maintenance strategies that fix problems and help them grow and adjust to market changes.
A shift from reactive to proactive maintenance offers a powerful solution. It makes the whole process more predictable. It also reduces business risk through continuous monitoring of infrastructure performance, security flaws, and system bottlenecks.
Rethinking maintenance strategies saves more than just money. Leveraging cloud technologies enables organizations to roll out critical updates more quickly. Likewise, standardized workflows and analytics cut development and support overhead. All this helps businesses stay agile and reduces hassle down the road.
Maintenance happens one way or the other. Organizations can choose to plan for it and fix issues proactively or wait for a costly emergency. This fundamental decision separates successful enterprises from the rest in today’s digital world.
What Does It Mean to Shift from Projects to Programs in Application Maintenance?
Traditionally, software maintenance was treated as a series of separate projects, each with clear start and end dates. A newer approach reframes maintenance as a program. Program-driven maintenance creates continuous cycles of improvement. It makes sure IT efforts stay in line with changing business goals.
1. Program-Driven Maintenance Keeping Business and Tech in Sync
What if maintenance activities could stay connected to business needs instead of operating in isolation? Program-driven maintenance makes this possible. It establishes continuous communication between IT and business teams. This ensures that maintenance efforts directly support strategic goals.
The key difference is this: projects focus on delivering specific outputs, while programs coordinate multiple projects to maximize organizational benefits in the long run. This distinction turns maintenance from reactive firefighting into a strategic activity that consistently drives value.
The program approach treats applications as evolving business tools that need constant attention. Program managers strive to strike a balance between short-term stability and long-term value creation when working on their systems. They make sure maintenance tasks fulfil immediate needs while not losing sight of the strategic direction.
2. Strategic Benefits of Program-Driven Maintenance
Program-driven maintenance offers many strategic advantages. Organizations gain agility by adapting maintenance activities to changing market conditions and business needs. They can fix potential bottlenecks long before they affect performance. This helps boost scalability.
The approach introduces a forward-looking perspective that prevents maintenance costs from rising unexpectedly even as system demands increase. Application complexity becomes easier to handle when approached through a coordinated program rather than disconnected projects.
Organizations also gain resilience. When teams strategically manage their entire application portfolio, they become better prepared to handle disruptions. They focus on building lasting internal strengths that go beyond fixing isolated issues. They can also direct resources toward projects that bring the most value. This delivers significant competitive advantages.
The biggest benefit of moving to program-driven maintenance is the way it changes organizations’ perceptions of their IT departments. IT shifts from being viewed as a cost center to being recognized as a strategic value driver. Over time, this change receives a boost as maintenance consistently delivers measurable results.
Thrive in the Digital Landscape with Application Modernization
How Much Does It Cost to Maintain an Application Today?
Maintenance includes both predictable and variable costs. These expenses change throughout an application’s life cycle. Maintenance costs typically stabilize as applications mature.
The annual costs of maintaining an application run between 15% and 20% of the original development budget. Therefore, if an application’s development cost is around $100,000, it would need about $15,000-$20,000 yearly for upkeep.
The first year’s maintenance costs are substantially higher, up to 50% of the original development costs. This happens because teams need money to fix unexpected problems and ensure that everything runs smoothly. After this period, costs usually settle at the 15-20% standard for later years.
Organizations should set aside $2,000 to $2,500 per month to maintain a typical application. This will help them cover all fundamental services like hosting. The following section breaks down these expenses.
I. Hosting
Hosting fees range from $70-$320 per month, depending on data storage needs and traffic volume. Applications that handle large datasets need more powerful infrastructure, which raises these costs.
II. Bug Fixes and Updates
Bug fixes and updates take up a large part of maintenance budgets. Minor fixes cost around $50-$500 to resolve, whereas major functional updates range from $1,000-$3,000 based on complexity. Security updates are another critical investment that costs $500-$2,000 per month.
III. Integrations
Integrations introduce significant ongoing expenses. API maintenance needs about $500 yearly, plus subscription costs for specific services. Payment gateway integrations cost approximately $149 monthly, plus additional per-transaction fees.
IV. Monitoring and Analytics
Monitoring tools and analytics services range from free tools to premium solutions costing $80 or more monthly. These tools provide essential insights into application performance, user behavior, and potential issues.
Even the best-designed applications need constant care to stay secure and perform well. For this reason, maintenance costs require the same attention as development costs during technology planning.
The Ultimate Guide to Modernizing your IBM i Applications
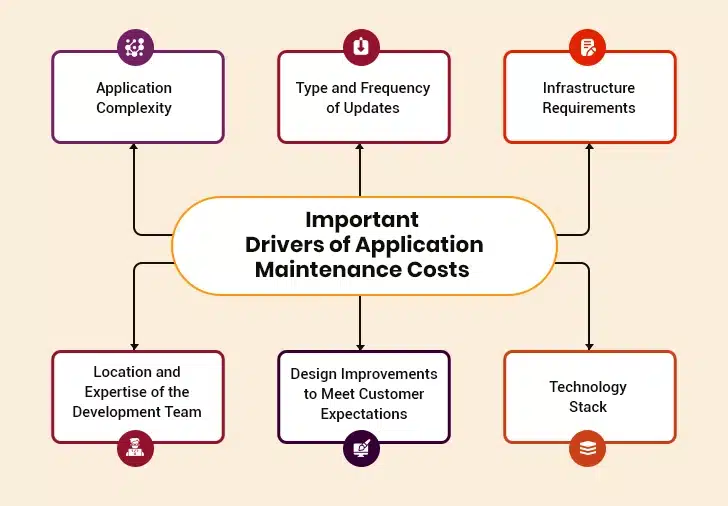
What Are the Factors That Influence the Cost of Maintaining an Application?
Many factors shape maintenance expenses. IT leaders who understand these cost drivers create more effective budgets and maintain greater control over their finances.
1. Application Complexity
There is a direct relationship between the complexity of an application and its maintenance costs. Simple applications with limited features require minimal upkeep. Complex systems demand significant investment due to their intricate architecture.
Modular design helps manage costs related to complexity. When applications are built with independent components, developers can modify one part without touching others. This is cheaper and easier than working with tightly connected systems, where a single change can cause unexpected problems anywhere.
2. Type and Frequency of Updates
The nature and frequency of updates impact maintenance costs. Bug fixes, patches, and new features carry different cost profiles, based on their complexity and importance to the business.
Many times, market pressure drives the update frequency. Users expect more as they become conversant with an application and want it to keep improving. Competitors continually raise performance standards. This creates pressure to enhance applications even when no immediate technical issues exist.
3. Infrastructure and Hosting Requirements
Hosting and infrastructure are unavoidable expenses in application maintenance. These costs vary based on data volume, traffic patterns, and performance needs. A simple application with low traffic may require only basic hosting. Complex applications need a powerful infrastructure that is significantly more expensive.
Applications that handle vast amounts of data require more robust and costly infrastructure. Similarly, applications serving global users need distributed hosting solutions to maintain performance across different geographical regions.
4. Development Team Location and Expertise
Developer expertise and location significantly affect app maintenance costs. Senior developers command higher rates but produce more efficient code that lowers expenses in the long run. Junior developers generally have lower hourly rates. However, they can create quality issues that need to be fixed later.
Location also plays an important role in deciding costs. Teams that are distributed globally can provide support around the clock, but face communication challenges. Cultural differences, regulatory complexities, and changing exchange rates affect total costs for global teams.
5. UI/UX Improvements to Meet User Expectations
User experience also affects maintenance costs. Poor UI/UX choices generally result in expensive fixes later. In contrast, investment in thoughtful design keeps customers happy, generates fewer support tickets, and reduces rework costs.
Good design speeds up product development. Teams that use consistent designs can release updates more quickly and adapt to market changes more easily. This further reduces maintenance efforts and costs.
How Can Enterprises Manage Application Maintenance Costs Strategically?
Managing costs for software maintenance needs an approach that aligns technical decisions with business goals. Companies that want to reduce their maintenance costs need strategies that improve long-term value.
I. Smart Development Decisions
Cross-platform development helps control maintenance costs, as it utilizes a single codebase for multiple platforms. Teams only need to implement updates once. They do not need to replicate work across platforms.
Building a minimum viable product (MVP) also helps. An MVP reduces maintenance by avoiding unnecessary features. Teams gather user feedback early, which guides development and focuses effort on what users actually need. The approach maximizes learning while reducing wasted effort.
II. Prioritization
Maintenance priorities should be guided by business impact. Teams can use risk-based matrices to assess the severity of issues and decide which problems need immediate attention. This allows resources to be allocated to high-value initiatives that address genuine business needs.
III. Rationalize Your Application Portfolio
Application rationalization cuts maintenance costs substantially. Teams evaluate all the applications to decide which ones to keep, upgrade, or retire. They study the business value and maintenance cost of each app. The practice helps them eliminate redundant systems and operate more efficiently.
IV. Embrace Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance makes use of analytics to detect potential system issues before they lead to failure. This lowers the cost of emergency fixes and reduces instances of unplanned downtime. The result? Teams can run their applications reliably and control maintenance expenses effectively.
| Strategy | How It Controls Cost |
|---|---|
| Cross-Platform Development | Cuts duplication. Updates are made only once. |
| Minimum Viable Product | Avoids maintaining costly, unused features. |
| Prioritization | Directs resources to the most valuable fixes. This helps improve return on investment. |
| Predictive Maintenance | Prevents expensive emergency repairs and reduces downtime. |
The Final Word
Maintaining applications is no ordinary expense. It is a tool that creates a competitive advantage when properly managed. Traditional software support often fails to meet the requirements of modern enterprises. It consumes a big portion of development budgets and delivers disappointing returns. A shift from project-based to program-driven maintenance enables them to transform maintenance into a real value driver.
There is no doubt that application maintenance will remain a significant budget item for enterprises. Companies that view maintenance as an investment rather than an expense will gain an edge. They will create applications that adapt to market changes quickly while maintaining financial efficiency.